Greening BC Skylines Together...
Green infrastructure (GI) can be defined as a strategically planned network of natural and semi-natural areas that are designed and managed to deliver a wide range of ecosystem services, while enhancing biodiversity, and quality of life. Ecosystem services include, but are not limited to: water purification and infiltration, air quality, urban cooling, fire suppression, climate mitigation and adaptation, green jobs, and connectivity of natural areas.
GI includes, but is not limited to: vegetated (green) roofs, living walls and facades, rain gardens, trees, parks, gardens, wetlands. Given the integration between water and land, these systems are also referred to as blue-green infrastructure.
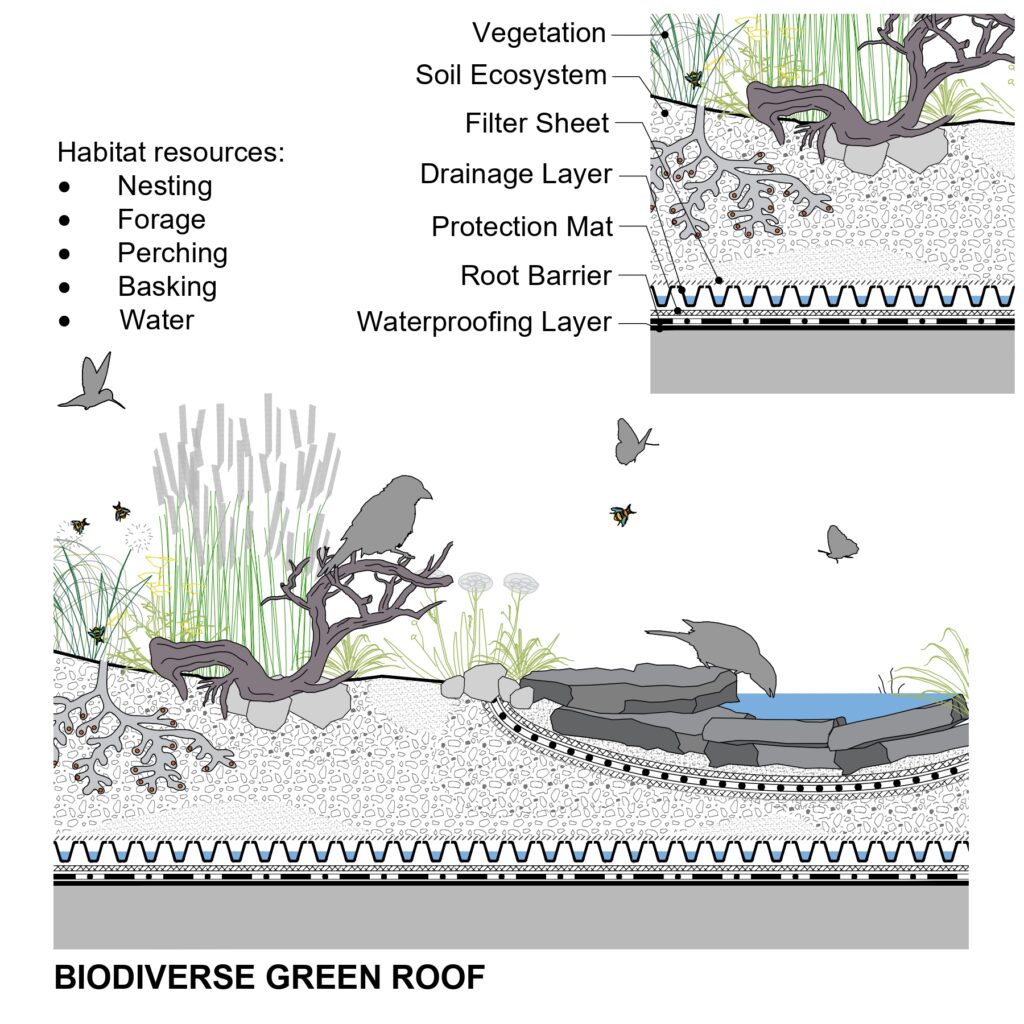
The image below applies to constructed ecosystems, like rain gardens, urban water features and green roofs, which use similar materials, more or less. Green roofs are the most technical of these, with additional protective layers that are not necessarily required at grade. This is not a technical drawing but an infographic to communicate the potential for biodiversity by green infrastructure.